Data
|
Proportion: Proportion, means the ratio between the density of material and water. Density, means the weight of unit volume. About the proportion of plastic, lighter proportion like polymethylpentene(0.83), heavier proportion like polytetrafluoroethene(2.3), others are almost about 1. The determine of proportion depends on ASTM D792(water displacement method). Molecular weight: The molecular weight of general compound is constant, but the molecular weight of polymer is in uneven size, so it has to use average value and the degree of distribution to indicate. These numerical can be measured by ASTM D3598(Standard Test Method for Citrate in Synthetic Detergents) Viscosity: Viscosity usually used to show the behavior of TPE or colloidal solution. It usually depends on ASTM D1823 or D1824. Bulk density & Particle size distribution: These numerical can show the particle size and tightness of plastic materials. Particle size distribution depends on ASTM D1921(Sieving) to measured. Bulk density depends on ASTM D1895 to measured. Free monomer content: Free monomer content can show the degree of polymerization of resin, always show by % or ppm. Water absorption: Water absorption shows the level about how plastic absorb moisture. About the test method, first, drying the sample and weigh it. Put it in water, after 24 or 48 ours, take out and weight it again. Count the percentage about how much the weight increased, then get water absorption. In plastic materials, phenolic resin, urea-formaldehyde resin, nylon, cellulosic resin have higher water absorption, olefin such as PE or PP, has lower water absorption. If the water absorption is too high, it will affect journal of mechanical strength and dimension stability easily. Air permeability: Air permeability shows the difficulty of plastic materials to through object, depends on ASTM D143 to get. Mechanical Properties Tensile Strength & Elongation: Tensile strength, means the intensity of force to stretching plastic materials into a certain degree, usually shows by how much force each unit area has. By stretching, plastic’s percentage of length is called elongation. Test piece, like picture1-1, usually used in tensile strength test. The stretching speed is 5.0~6.5mm/min. Details methods can refer to ASTM D638.
Bending Strength: Bending strength is to determine plastic’s folding endurance, depends on ASTM D790 to measured. It usually shows by how much force each unit area has. PVC, MF, Epoxy, Polyester have good bending strength. Glass fiber usually used to up plastic’s folding endurance. Compression Strenght: Compression strength means the capability when plastic bear external compressive force, depends on ASTM D695 to measured. Impact Strength: Impact strength means the strength when plastic bear external strike force. There are two test Methods in ASTM D256, Charpy method & Izod method. The count of impact strength in ASTM showed by the energy needed to destroy the specimen divided by temperature of test piece. Each country has different standards. In some Europe country, divided by breaking point cross-sectional area to show it. PVC, PE, PP, ABS have higher impact strength. Hardness: Plastic’s hardness usually depends on Rock well Druometer Method(ASTM D785), Barcol Impressor Method(ASTM D785), or Shore Durometer Method(ASTM D2240)to get. By using a steel ball in predetermined size, put it into test piece at a predetermined pressure to see how deep the steel ball can go into, use the deepness to show the hardness. Rock well Druometer Method has different foot mark to correspond test pieces with different hardness. For plastic, it has three type to use:R(ball diameter:12.7mm, load:60kgf), M(ball diameter:6.35mm, load:100kgf), E(ball diameter:3.175mm, load:100kgf). Coefficient of Elasticity(Tensile Elastic Modulus): Coefficient of elasticity is to show the capability for restore the original shape when plastic deformed by external force. It usually shows by ratio of stress. Besides, we also use bending elasticity and compression elastic modulus to show it. When the elasticity is bigger, it means the plastic’s rigidity is better. Thermal Properties Plastic’s thermal properties means how plastic change when affected by temperature. Usually, it has most closely relationship between thermal properties and plastic processing. Important items as the following: Heat Deflection Temperature: Also called HDT. As ASTM D648 methods, HDT means to make test piece at a certain pressure and heating rate, to see how much the temperature is when test piece bend to some level. HDT shows that if plastic can keep it’s shape when it meet high temperature and pressure. Vicat Softening Point: Vicat softening point deponds on ASTM D1525. To exert a certain load(1kg)on a flat tip(about 1mm2 size), warming it by promote the temperature 50℃ every hour. When flat tip’s depth of immersion go to 1mm, the temperature called vicat softening point. It means the temperature when plastic be warmed to start to flow. Heat Conductivity: Heat conductivity means the rate when heat be transmited in plastic, depends on ASTM C177 to measured. The lower heat Conductivity is, means insulation is better. Plastic filled up by metallic minerals or glass fiber has better heat conductivity, plastic filled up by flour has lower heat conductivity. Expandable plastic usually make heat conductivity lower. Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Thermal expansion coefficient is the ratio when plastic’s size swell during warming, depends on ASTM D696 to measured. Plastic’s thermal expansion coefficient is higher then metal about 2~10 times, when design appliance which use plastic and metal at the same time, it has to consider exhaustively to avoid cracking by internal stress. Shrinkage: Shrinkage means the proportion of plastic’s after-shrinking size and original design size, depends on ASTM D955 to measured. When designing plastic module, it must to consider the shrinkage at first, to avoid the error between module size and end product size. Melt Index: Melt index, is a method to show the fluidity of gel. The test method is to use melt index count at a certain temperature and pressure, let gel to flow out from a small hole with certain length and caliber, after a while, weigh it, then get the melt index. It usually can be used to determine thermoplastic plastics’ processing properties. Melting point: Melting point means the temperature when crystalline materials be destroy. Glass Transition Point: When constituent molecule segment begin to vibrate, changing from solid to fluid, the temperature transfer point is called glass Transition Point. Chemical Properties Chemical properties shows the properties when plastics deteriorated by chemical material, solvent or another effect of chemical changes. Important items as the following: Solvent Resistance: Put plastics in solvent at a certain temperature, after a while, determine the change of weight, volume, tensile strength and elongation. Plastic which has the smallest variation has better solvent resistance. Flammability: Plastics’ flammability is to determine the test piece’s burning rate and self-extinguishing effect. PTFE, PVC, Nylon have flammability, Polyethylene, Polypropylene and Polystyrene are easier to burn. To improve plastics’ flammability, usually add flame retardants in plastics. We can use JIS A1321, ASTM D 229, D508, D757, E84, JISK 6911, K6918 to check it. Weather Resistance: When putting plastics outside, plastics could be deteriorated by the weather(light, hot, air, rain). Weather resistance is to show the resistance how plastic can resist the weather, including in UV, oxygen, ozone. The test methods are outdoor exposure method(depends on ASTM D1435) and artificial promotion method(depends on ASTM D1499). |

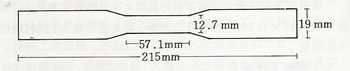 picture 1-1 Test piece for tensile strength test
picture 1-1 Test piece for tensile strength test